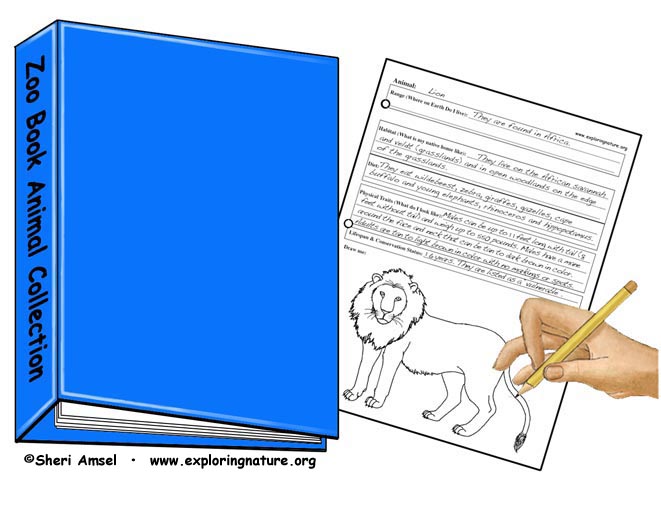
Before you go to the zoo, learn about the animals you will see in the zoo exhibits. Using the links below discover each animal's range, habitat, diet, body traits, lifespan and conservation status. Think about its role in its habitat and food web.
Choose 10 of your favorite animals and using the zoo animal graphic organizer, put together a "Zoo Book Animal Collection". Use the animal drawing or coloring links to illustrate your zoo book.
Choose a specific habitat exhbited at the zoo and using the animals you have researched, create a food web for that ecosystem. Use the food web resources on Exploring Nature to help fill out the species in your food webs.
Here are some common animal exhibits at zoos worldwide:
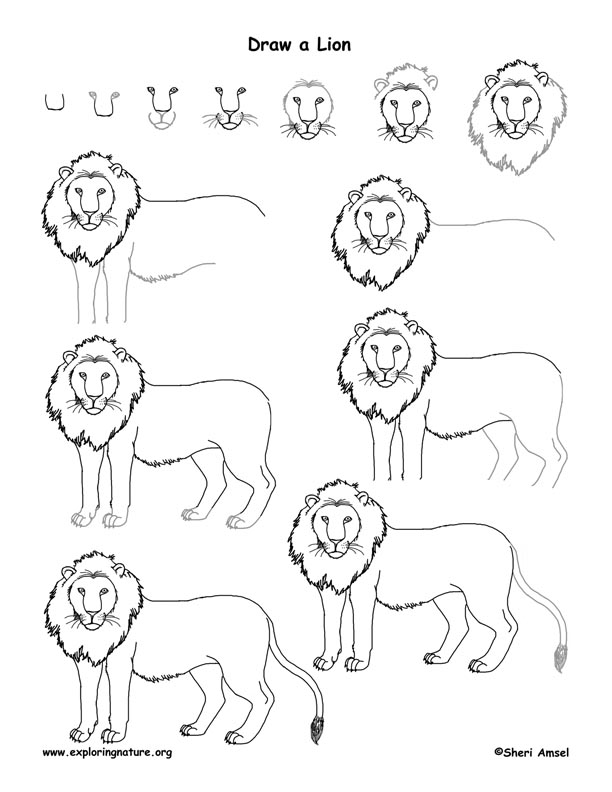
The African Plains Exhibit may feature lions, zebras, the baboon, giraffe. Learn to draw a lion, zebra, baboon, giraffe using these links for your zoo book collection.
The North American Plains Exhibit may feature American bison, pronghorn antelope and prairie dogs. Print out and color a bison and prairie dog here.
The Aquatic Bird House may feature the puffin and flamingo. Draw the flamingo too.
The Bear Exhibit may feature the grizzly and polar bear. Draw a polar bear and cut out and color a grizzly.
The Birds of Prey Exhibit may feature the snowy owl, barred owl and bald eagle. Learn to draw the bald eagle here. Print out and color the barred owl here.
The monarch butterfly may be featured in the Butterfly Garden. Print out and color the monarch life cycle.
The Reptile House may feature the American alligator, the anaconda and the komodo dragon. Learn to draw the alligator and anaconda here. Print out and color a komodo here.
The Ocean Mammals Exhibits may feature the California sea lion. Print out and color a sea lion here. It may also feature sea otters.
The Animals of the Andes Exhibit may feature the chinchilla. Print out and color a chinchilla here.
The Madagascar! Exhibit may feature the fossa, Nile crocodile, ring-tailed lemur and red ruffed lemur. Print out and color the fossa and ring-tailed lemur here.
The African Rainforest Exhibit may feature gorillas and learn to draw gorillas here. See and learn about the okapi and learn to draw one here.
The Himalayan Highlands Exhibit may feature the red panda and snow leopard. Print out and color the snow leopard here.
Other Asian Habitat Exhibits may feature tigers. You can draw a tiger for your zoo book. Or you may see the giant panda. Or the Asian elephant. Learn to draw elephants here.
Here is an example a completed lion Zoo Animal Graphic Organizer Page and a lion Drawing Activity:
Disciplinary Core Ideas:
LS1.A: Structure and Function
• Plants and animals have both internal and external structures that serve various functions in growth, survival, behavior, and reproduction. (4-LS1-1)
LS2.A: Interdependent Relationships in Ecosystems
• There are many different kinds of living things in any area, and they exist in different places on land and in water. (2-LS4-1)
• The food of almost any kind of animal can be traced back to plants. Organisms are related in food webs in which some animals eat plants for food and other animals eat the animals that eat plants.
• Organisms, and populations of organisms, are dependent on their environmental interactions both with other living things and with nonliving factors. (MS-LS2-1)
LS2.C: Ecosystem Dynamics, Functioning, and Resilience
• Ecosystems are dynamic in nature; their characteristics can vary over time. Disruptions to any physical or biological component of an ecosystem can lead to shifts in all its populations. (MS-LS2-4)
• Biodiversity describes the variety of species found in Earth’s terrestrial and oceanic ecosystems. The completeness or integrity of an ecosystem’s biodiversity is often used as a measure of its health. (MS-LS2-5)
LS2.D: Social Interactions and Group Behavior
• Being part of a group helps animals obtain food, defend themselves, and cope with changes. Groups may serve different functions and vary dramatically in size (Note: Moved from K–2). (3-LS2-1)
LS4.D: Biodiversity and Humans
2-LS4-1.P Make observations of plants and animals to compare the diversity of life in different habitats.
Performance Expectations:
2-LS2-1. Make observations of plants and animals to compare the diversity of life in different habitats.[Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on the diversity of living things in each of a variety of different habitats.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include specific animal and plant names in specific habitats.]
4-LS1-1. Construct an argument that plants and animals have internal and external structures that function to support survival, growth, behavior, and reproduction. [Clarification Statement: Examples of structures could include thorns, stems, roots, colored petals, heart, stomach, lung, brain, and skin.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment is limited to macroscopic structures within plant and animal systems.]
4-LS1-2. Use a model to describe that animals receive different types of information through their senses, process the information in their brain, and respond to the information in different ways. [Clarification Statement: Emphasis is on systems of information transfer.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include the mechanisms by which the brain stores and recalls information or the mechanisms of how sensory receptors function.]
ETS1.B: Developing Possible Solutions
• Designs can be conveyed through sketches, drawings, or physical models. These representations are useful in communicating ideas for a problem’s solutions to other people. (secondary to 2-LS2-2)
Common Core State Standards Connections:
ELA/Literacy
W.2.7 Participate in shared research and writing projects (e.g., read a number of books on a single topic to produce a report; record science observations). (2-LS4-1)
W.2.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. (2-LS4-1)RI.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. (3-LS2-1)
RI.5.7 Draw on information from multiple print or digital sources, demonstrating the ability to locate an answer to a question quickly or to solve a problem efficiently. (5-LS2-1)
SL.4.5 Add audio recordings and visual displays to presentations when appropriate to enhance the development of main ideas or themes. (4-LS1-2)
SL.5.5 Include multimedia components (e.g., graphics, sound) and visual displays in presentations when appropriate to enhance the development of main ideas or themes. (5-LS2-1)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Zoo Activity - Before You Go to The Zoo Animal Research" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Zoo-Activity-Before-You-Go-to-The-Zoo-Animal-Research >