* Our Advanced Anatomy content is developed for High School and/or Introductory College Level Students.
Systemic Circulation
Function: Brings oxygenated blood supply to all the body’s tissues, delivers nutrients from digestive tract to tissues and carried away CO2 and metabolic waste.
Oxygen rich blood is pumped from the heart via:
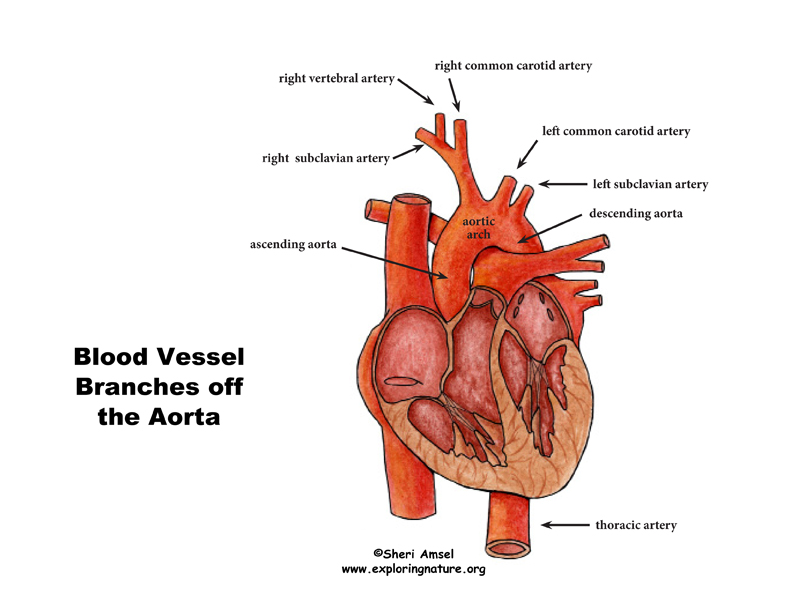
> left ventricle through the semilunar valve* into the ascending aorta (*Opposite each semilunar valve cusp is an aortic sinus which contains pressoreceptors involved in blood pressure regulation. The semilunar valve prevents the back flow of blood back into the heart.)
> the ascending aorta arches up (in front of pulmonary trunk) and gives off right and left coronary arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the heart muscle itself.
> Then the ascending aorta becomes the aortic arch
> the aortic arch then gives off the brachiocephalic trunk (under right clavicle)
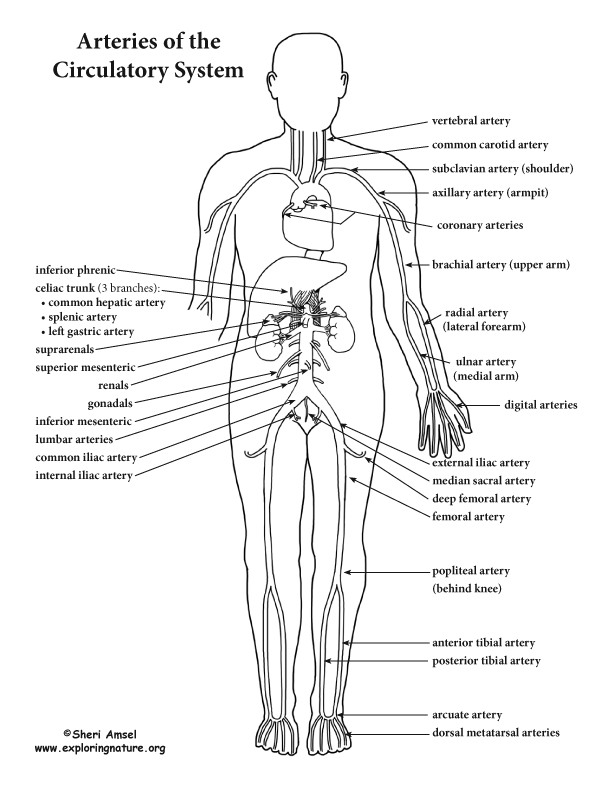
> the brachiocephalic trunk branches into the right common carotid artery (which supplies blood to the right side of the neck and head) and right subclavian artery (which supplies blood to the right upper limb - arm) (See Head and Neck Circulation and Upper Limb Circulation for that content).
> Next the aortic arch gives off the left common carotid artery (which supplies blood to the left side of the neck and head) and then the right subclavian artery (which supplies blood to the left upper limb - arm) (See Head and Neck Circulation and Upper Limb Circulation for that content).
> Then the aortic arch becomes the descending aorta
> The descenting aorta turns into the thoracic aorta and gives off branche to the organs of the chest
> Then the thoracic aorta passes through the diaphram and becomes the abdominal aorta
> The abdominal aorta supplies blood to the organs of the abdominal and pelvic region (including stomach, kidneys, liver, adrenal glands, etc.) (See Thoracic and Abdominal Circulation for that content).
> The abdominal aorta splits in the pelvis into the common iliac artieries, which supply blood to the lower limbs (See Lower Limb Circulation for that content).
For assessment, try the Blood Vessel Labeling Activity.