They are found in ocean waters that are not too cold and not too hot (temperate) all around the world.
They live mostly in shallow waters (less than 65 feet deep) near shorelines.
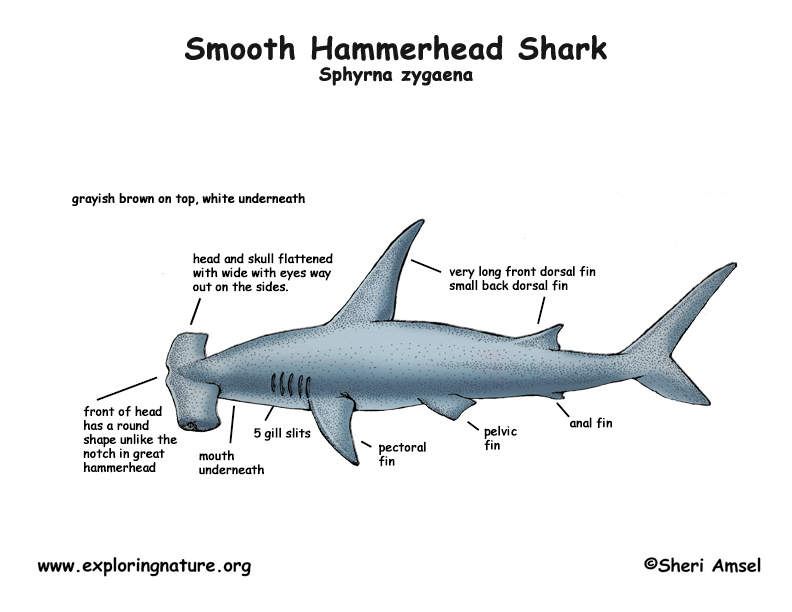
They have a weird, shortened head with two long sides to it and the eyes perched out on the ends. The mouth is underneath, facing downward as they swim. The smooth hammerhead has a rounded front to their head, which differs from the great hammerhead that has a notch there. They have a tall front dorsal fin. Like most sharks they are dark on top and light underneath. They can reach 16 feet long and weigh up to 900 pounds.
Young hammerheads often school together in big groups while adults live alone. In hot weather they may migrate north, swimming close to the surface of the water with their dorsal fin showing.
They eat fish, smaller sharks, and stingrays.
Females are pregnant for up to 11 months (gestation). Their eggs will hatch inside the female so they give birth to 20-40 live young (viviparous) in the summer.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Chondrichthyes
Subclass: Elasmobranchii
Order: Carcharhiniformes
Family: Sphyrnidae
Genus: Sphyrna
Species: S. zygaena
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Shark (Smooth Hammerhead)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Shark-Smooth-Hammerhead >