They are found in mild to tropical oceans around the world.
They live in open water and don't come to coastal waters very much.
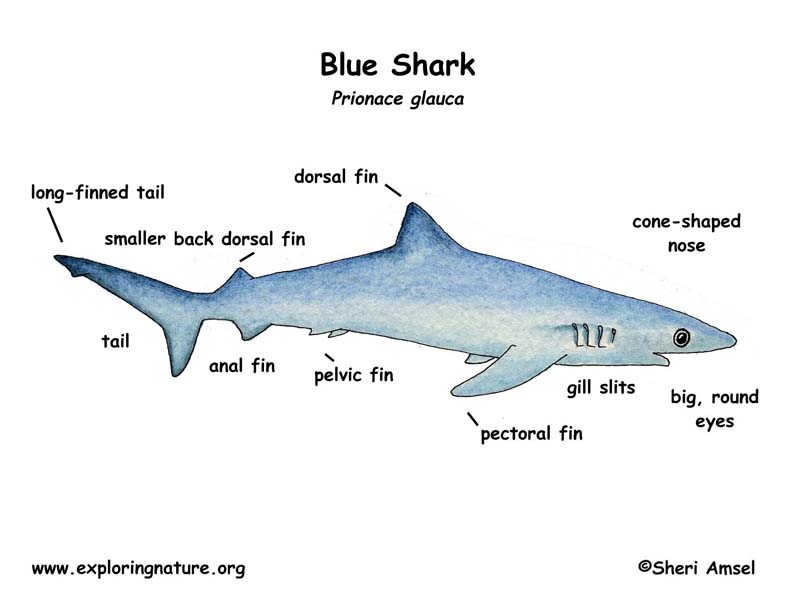
The blue shark has a long, thin body with a cone-shaped nose, 5 gill slits on each side and long front (pectoral) fins. They have big, round eyes and grow to ten feet long. Their backs and sides are blue and they are white underneath.
They rarely swim in shallow water, so don't attack people swimming at the beach. However, they might attack people in open water (ship wreck victims). They are thought to migrate long distances. They have been known to be attacked and eaten by California sea lions and larger sharks.
They are surface predators and eat mostly small fish and squid.
Females are pregnant for 9-12 months (gestation). Then they give birth to 25-100 live young (viviparous) - not eggs.
They are not endangered. In their range and habitat, they are very common.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Chondrichthyes
Order: Carcharhiniformes
Family: Carcharhinidae
Genus: Prionace
Species: P. glauca
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Shark (Blue)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://exploringnature.org/db/view/Shark-Blue >