They are found throughout South East Asia, Australia, Japan and some Pacific islands (including Hawaii).
They live in shallow water on coral reefs and coastlines, though they can attach to drifting plant mats that float out in the open ocean.
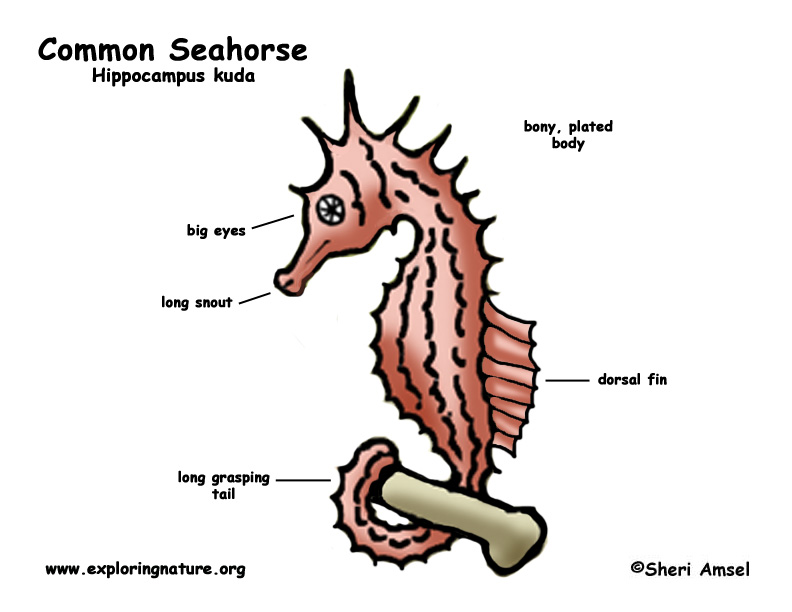
They hold their bodies upright and watch for prey with eyes that can move separately from each other. They have fins that sway to move them from place to place and a tail that can wrap around things (prehensile) to anchor them. They have no scales but only skin over their boney plate skeleton. Their cream-colored skin has dark spots and some species can change color to match their surroundings (camouflage). They have no teeth.
They use their camouflage to blend in and then wait for prey to swim by. Then they suck them into their tube-like mouth and swallow them whole. Seahorses bony-plates make them inedible to predators, but they have been over-collected by man.
They eat small ocean animals, like baby crabs and shrimp.
The male has a pouch on its belly, called the brood pouch. The female lays eggs into the male's pouch. The male then fertilizes the eggs and carries them for 3-4 weeks when the babies are born and begin their little lives on their own.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Actinopterygii
Order: Syngnathiformes
Family: Syngnathidae
Genus: Hippocampus
Species: H. zosterae
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Seahorse (Common) " Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Seahorse-Common- >