Cottontail rabbits are the most common and widely found rabbits in North America. There are several species of cottontail rabbit, the most common is the eastern cottontail. There is also a desert cottontail out in the dry (arid) western ranges.
Cottontail rabbits live on the edges of open fields, forests and wetlands. They like to hide in tall grass, thickets, and along fencerows.
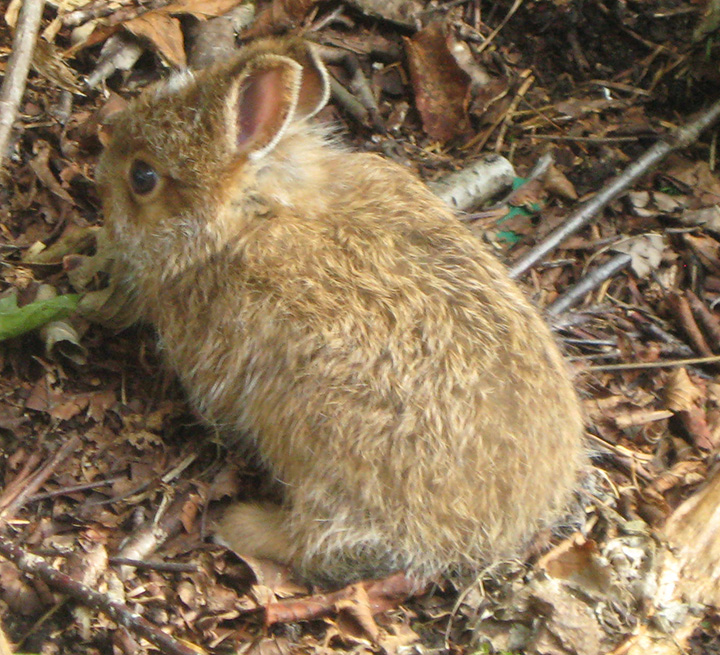
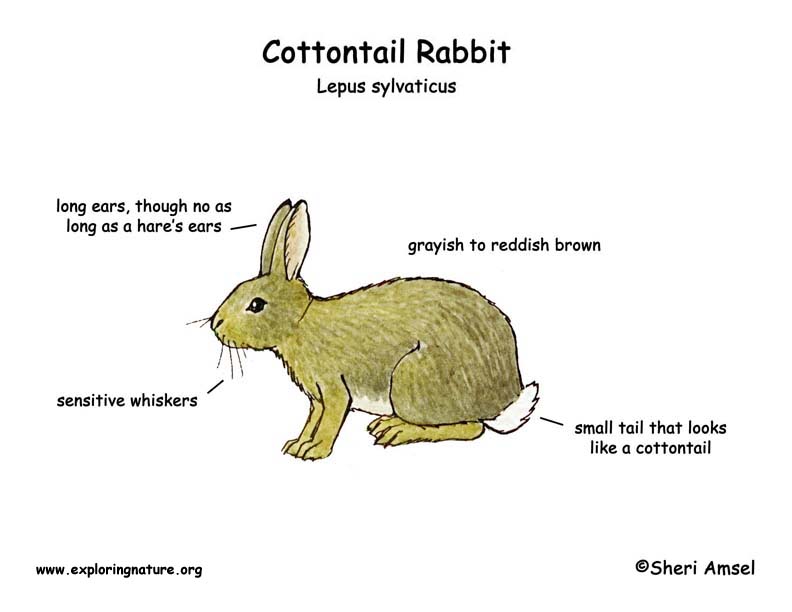
They have a rounded body with large back feet, long ears, and a round, white, fluffy tail. They vary in color from grayish to reddish brown and have white bellies. They weigh 2-3 pounds.
Cottontail rabbits are active all year, mostly at night (nocturnal). They have good sight and hearing and will freeze in place when sensing danger. Their coloring helps them blend in (camouflage). If they are flushed out of hiding they can run up to 18 mph for a short distance. If caught by a predator they can make a loud, shrill scream.
They eat grass and green plants and in winter will eat the bark, twigs, and buds of shrubs and young trees (herbivores).
They are an important food source for other animals, such as hawks, owls, coyote, fox and bobcat.
Females are pregnant for about 28 days (gestation) and give birth to 3-8 young in a nest built underground or under thick grass and lined with grass and fur. Females will mate again right after their young are born. From March to early fall females will have 2 - 4 litters. Only 1 in 5 bunnies survive their first year.
The average lifespan for cottontails is only 4 to 6 months. They are not threatened.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Lagomorpha
Family: Leporidae
Genus: Sylvilagus
Species: Lepus sylvaticus
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Rabbit (Cottontail)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Rabbit-Cottontail >