LS2.B: Cycle of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems
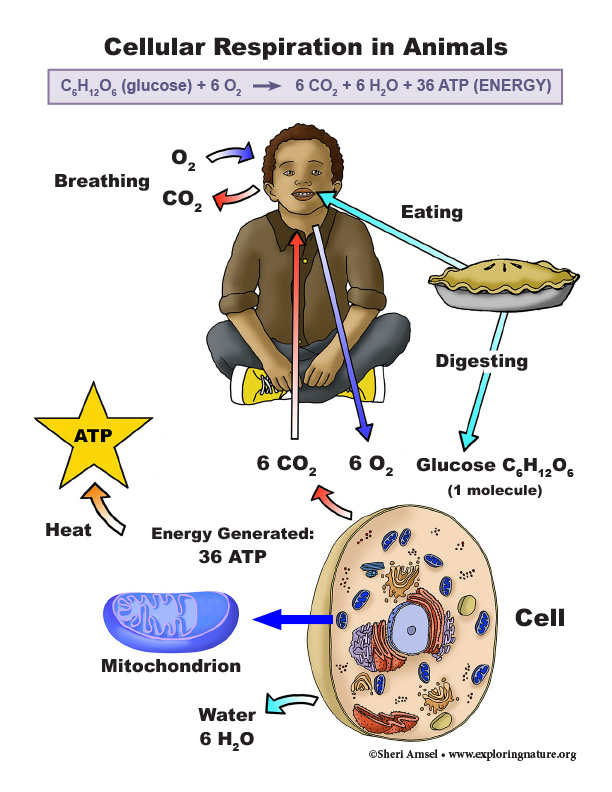
• Photosynthesis and cellular respiration (including anaerobic processes) provide most of the energy for life processes. (HS-LS2-3)
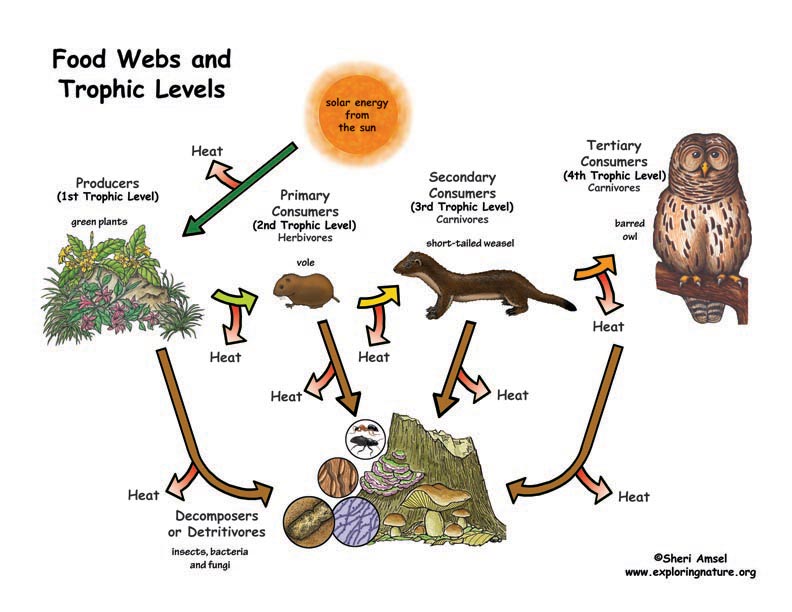
• Plants or algae form the lowest level of the food web. At each link upward in a food web, only a small fraction of the matter consumed at the lower level is transferred upward, to produce growth and release energy in cellular respiration at the higher level. Given this inefficiency, there are generally fewer organisms at higher levels of a food web. Some matter reacts to release energy for life functions, some matter is stored in newly made structures, and much is discarded. The chemical elements that make up the molecules of organisms pass through food webs and into and out of the atmosphere and soil, and they are combined and recombined in different ways. At each link in an ecosystem, matter and energy are conserved. (HS-LS2-4)
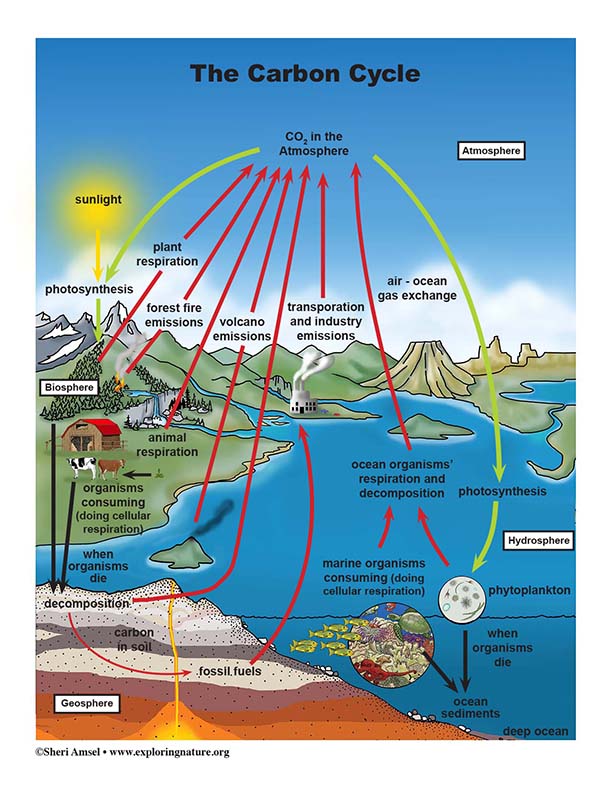
• Photosynthesis and cellular respiration are important components of the carbon cycle, in which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, atmosphere, oceans, and geosphere through chemical, physical, geological, and biological processes. (HS-LS2-5)
PS3.D: Energy in Chemical Processes
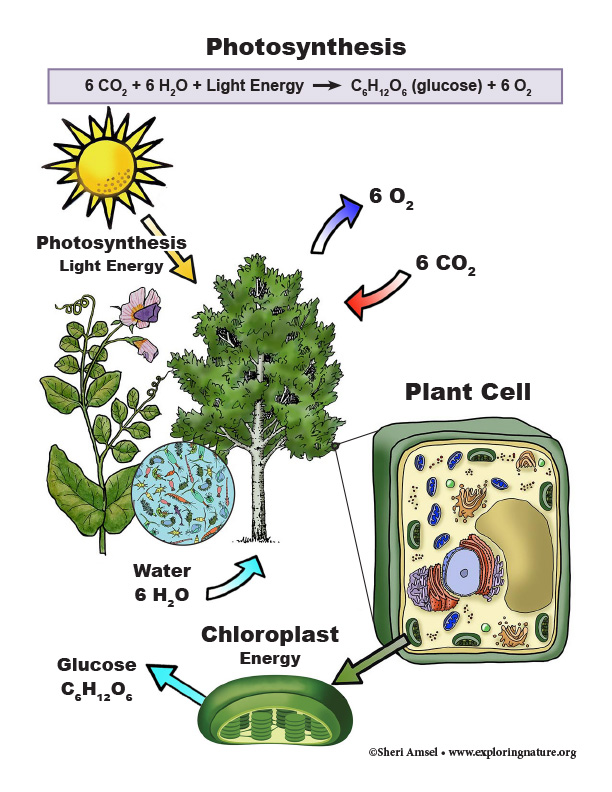
• The main way that solar energy is captured and stored on Earth is through the complex chemical process known as photosynthesis.(secondary)
Use the Template and Resource Links to Fulfill NGSS
l. Goals:
Essential Questions:
NGSS Note: Think, question, entertain ideas.
ll. Introductory Activities to Assess Prior Knowledge
A. Answer Questions - that assess students’ understanding of photosynthesis and cellular respiration as important components of the carbon cycle.
The Carbon Cycle - Short Answer Quiz
lll. New Knowledge - Text
A. Read about photosynthesis and cellular respiration as important components of the carbon cycle.
Breaking Down the Carbon Cycle
Read about: Cycles of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems
Read about: Photosynthesis
Read about: Cellular Respiration
B. Examples of Models (depicts the concept expressed in the reading):
Ask students to look at the models and explain how each illustrates the concepts they've read about.
A. Understanding how the Carbon Cycle works:
The Carbon Cycle - Parts and Processes Quiz
Cycles of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems - Short Answer Quiz
Biomass Performance Task - Cycling of Matter and Flow of Energy Among Organisms in an Ecosystem
B. Authentic Performance - Understanding by Design (UbD) assessment tool.
Use critical thinking to complete thse Authentic Performance Activities and deepen your understanding about the above topics.
The Meat Industry - Authentic Performance - Cycles of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "LS2.B: Cycles of Matter and Energy Transfer in Ecosystems (HS-LS2 Ecosystems: Interactions, Energy, and Dynamics)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/LS2B-Cycles-of-Matter-and-Energy-Transfer-in-Ecosystems-HS-LS2-Ecosystems-Interactions-Energy-and-Dynamics >