_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Disciplinary Core Ideas
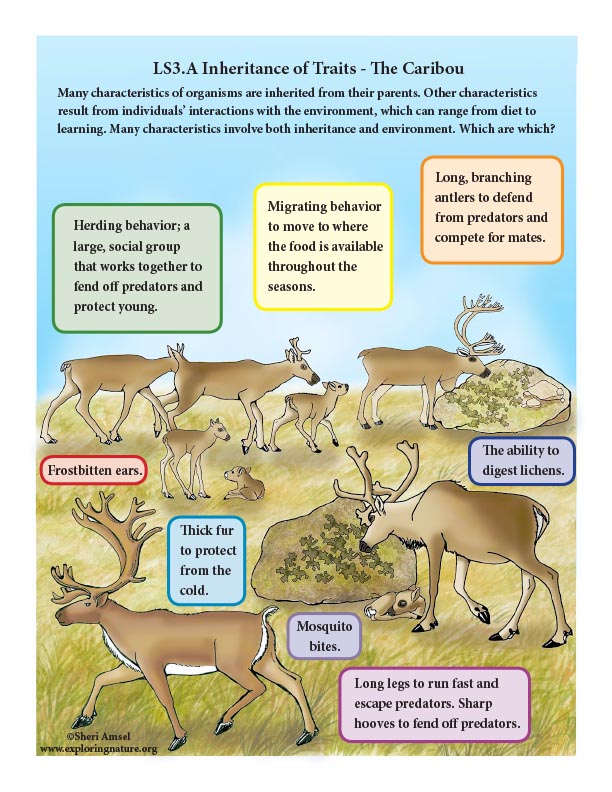
LS3.A: Inheritance of Traits
• Many characteristics of organisms are inherited from their parents. (3-LS3-1)
• Other characteristics result from individuals’ interactions with the environment, which can range from diet to learning. Many characteristics involve both inheritance and environment. (3-LS3-2)
LS3.B: Variation of Traits
• Different organisms vary in how they look and function because they have different inherited information. (3-LS3-1)
• The environment also affects the traits that an organism develops. (3-LS3-2)
Performance Expectations Students who demonstrate understanding can:
3-LS3-1. Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence that plants and animals have traits inherited from parents and that variation of these traits exists in a group of similar organisms.
3-LS3-2. Use evidence to support the explanation that traits can be influenced by the environment.
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Use the Template and Resource Links to Fulfill NGSS
l. Goals:
Essential Questions:
NGSS Note: Think, question, entertain ideas.
ll. Introductory Activities to Assess Prior Knowledge
A. Simple Activities - that assess students’ understanding of inherited characteristics vs. characteristic created by the environment.
Heredity of Traits - Matching
Variation of Traits in Dogs - Matching
Variation of Traits in Pea Plants - Matching
B. Brainstorming Session
Question: Which characteristics (traits) are inherited, created by the environment or both?
1. Break students down into groups of 3-4.
2. Ask students to generate a list of which traits are inherited, created by the environment or both.
3. Discuss
lll. New Knowledge - Text
Read about inherited and environmentally created traits and characteristics:
• Inheritance and Variation of Traits in Flowers - Authentic Performance
• Variation of Traits in Animals - Authentic Performance
Examples of Models (depicts the concept expressed in the reading):
• Ask students to create a model of inherited traits and environmentally affected traits. They can draw the model or create one using pictures they find online.
Assessment:
• Traits and Characteristics (Human) - Critical Thinking Activity
lV. Experiments, Activities, Model-making, Media (Critical Thinking)
Inquiry related to Inherited Traits:
• Genetics Activity - Create The Kids
• Variation of Traits in Pea Plants - Matching
• Variation of Traits - Plant Investigation
• Variation of Traits in Animals - Authentic Performance
• Inheritance and Variation of Traits in Flowers - Authentic Performance
V. Summarize Knowledge - Enduring Understandings
Vl. Next Generation of Science Standards (NGSS) - Grade 3
Disciplinary Core Ideas
LS3.A: Inheritance of Traits
• Many characteristics of organisms are inherited from their parents. (3-LS3-1)
• Other characteristics result from individuals’ interactions with the environment, which can range from diet to learning. Many characteristics involve both inheritance and environment. (3-LS3-2)
LS3.B: Variation of Traits
• Different organisms vary in how they look and function because they have different inherited information. (3-LS3-1)
• The environment also affects the traits that an organism develops. (3-LS3-2)
Science and Engineering Practices (NGSS)
Analyzing and Interpreting Data
Analyzing data in 3–5 builds on K–2 experiences and progresses to introducing quantitative approaches to collecting data and conducting multiple trials of qualitative observations. When possible and feasible, digital tools should be used.
• Analyze and interpret data to make sense of phenomena using logical reasoning. (3-LS3-1)
Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions
Constructing explanations and designing solutions in 3–5 builds on K–2 experiences and progresses to the use of evidence in constructing explanations that specify variables that describe and predict phenomena and in designing multiple solutions to design problems.
• Use evidence (e.g., observations, patterns) to support an explanation. (3-LS3-2)
Crosscutting Concepts (NGSS)
Patterns
• Similarities and differences in patterns can be used to sort and classify natural phenomena. (3-LS3-1)
Cause and Effect
• Cause and effect relationships are routinely identified and used to explain change. (3-LS3-2)
Performance Expectations
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
3-LS3-1. Analyze and interpret data to provide evidence that plants and animals have traits inherited from parents and that variation of these traits exists in a group of similar organisms.
[Clarification Statement: Patterns are the similarities and differences in traits shared between offspring and their parents, or among siblings. Emphasis is on organisms other than humans.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include genetic mechanisms of inheritance and prediction of traits. Assessment is limited to non-human examples.]
3-LS3-2. Use evidence to support the explanation that traits can be influenced by the environment.
[Clarification Statement: Examples of the environment affecting a trait could include normally tall plants grown with insufficient water are stunted; and, a pet dog that is given too much food and little exercise may become overweight.]
Common Core State Standards Connections:
ELA/Literacy
RI.3.1 Ask and answer questions to demonstrate understanding of a text, referring explicitly to the text as the basis for the answers. (3-LS3-1),(3-LS3-2)
RI.3.2 Determine the main idea of a text; recount the key details and explain how they support the main idea. (3-LS3-1),(3-LS3-2)
RI.3.3 Describe the relationship between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text, using language that pertains to time, sequence, and cause/effect. (3-LS3-1),(3-LS3-2)
W.3.2 Write informative/explanatory texts to examine a topic and convey ideas and information clearly. (3-LS3-1),(3-LS3-2)
SL.3.4 Report on a topic or text, tell a story, or recount an experience with appropriate facts and relevant, descriptive details, speaking clearly at an understandable pace. (3-LS3-1),(3-LS3-2)
Mathematics
MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (3-LS3-1),(3-LS3-2)
MP.4 Model with mathematics. (3-LS3-1),(3-LS3-2)
3.MD.B.4 Generate measurement data by measuring lengths using rulers marked with halves and fourths of an inch. Show the data by making a line plot, where the horizontal scale is marked off in appropriate units—whole numbers, halves, or quarters. (3-LS3-1),(3-LS3-2)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Grade 3 - 3-LS3 Heredity: Inheritance and Variation of Traits" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Grade-3-3-LS3-Heredity-Inheritance-and-Variation-of-Traits >