_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Disciplinary Core Ideas
PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter
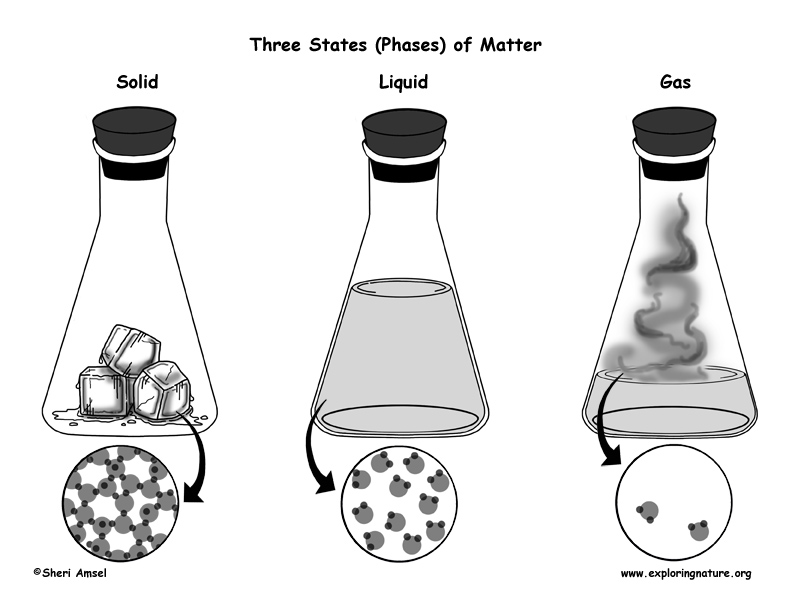
• Different kinds of matter exist and many of them can be either solid or liquid, depending on temperature. Matter can be described and classified by its observable properties. (2-PS1-1)
• Different properties are suited to different purposes. (2-PS1-2),(2-PS1-3)
• A great variety of objects can be built up from a small set of pieces. (2-PS1-3)
PS1.B: Chemical Reactions
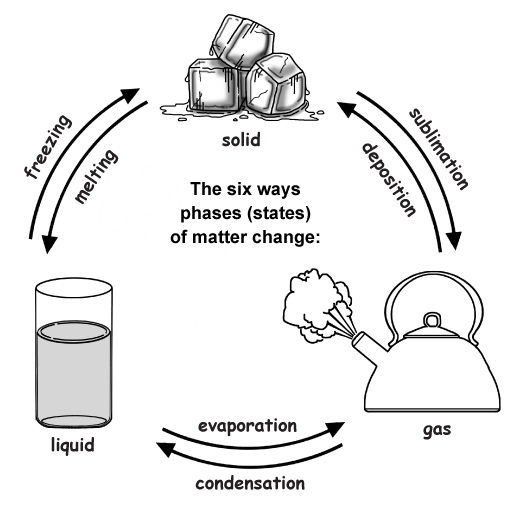
• Heating or cooling a substance may cause changes that can be observed. Sometimes these changes are reversible, and sometimes they are not. (2-PS1-4)
Performance Expectations: Students who demonstrate understanding can:
2-PS1-1. Plan and conduct an investigation to describe and classify different kinds of materials by their observable properties. [Clarification Statement: Observations could include color, texture, hardness, and flexibility. Patterns could include the similar properties that different materials share.]
2-PS1-2. Analyze data obtained from testing different materials to determine which materials have the properties that are best suited for an intended purpose.* [Clarification Statement: Examples of properties could include, strength, flexibility, hardness, texture, and absorbency.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment of quantitative measurements is limited to length.]
2-PS1-3. Make observations to construct an evidence-based account of how an object made of a small set of pieces can be disassembled and made into a new object. [Clarification Statement: Examples of pieces could include blocks, building bricks, or other assorted small objects.]
2-PS1-4. Construct an argument with evidence that some changes caused by heating or cooling can be reversed and some cannot. [Clarification Statement: Examples of reversible changes could include materials such as water and butter at different temperatures. Examples of irreversible changes could include cooking an egg, freezing a plant leaf, and heating paper.]*
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Use the Template and Resource Links to Fulfill NGSS
l. Goals:
Essential Questions:
ll. Introductory Activities to Assess Prior Knowledge
A. Simple Activities - that assess students’ understanding of the phases of matter.
States of Matter - Matching (K-4)
B. Analyzing Matter: Give students 5 objects to "analyze," i.e. sponge, block of wood, wax candle, ball of yarn, square of cheese. Ask them to:
Analyzing Matter Activity
C. Brainstorming Session
Question: Thinking about materials and their properties.
1. Break students down into groups of 3-4.
2. Ask students to generate a list of the different materials that exist is at least two phases (liquid, solid, gas).
3. Discuss
Inquiry related to state of matter.
Rain Making Activity - The Water Cycle
Cloud Making Activity - How Do Clouds Form?
V. Summarize Knowledge - Enduring Understandings
Vl. Next Generation of Science Standards (NGSS) - Grade 2
Disciplinary Core Ideas
PS1.A: Structure and Properties of Matter
Science and Engineering Practices (NGSS)
Planning and Carrying Out Investigations
Planning and carrying out investigations to answer questions or test solutions to problems in K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to simple investigations, based on fair tests, which provide data to support explanations or design solutions.
• Plan and conduct an investigation collaboratively to produce data to serve as the basis for evidence to answer a question.(2-PS1-1)
Analyzing and Interpreting Data
Analyzing data in K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to collecting, recording, and sharing observations.
• Analyze data from tests of an object or tool to determine if it works as intended. (2-PS1-2)
Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions
Constructing explanations and designing solutions in K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to the use of evidence and ideas in constructing evidence-based accounts of natural phenomena and designing solutions.
• Make observations (firsthand or from media) to construct an evidence-based account for natural phenomena. (2-PS1-3)
Engaging in Argument from Evidence
Engaging in argument from evidence in K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to comparing ideas and representations about the natural and designed world(s).
• Construct an argument with evidence to support a claim. (2-PS1-4)
Connections to Nature of Science
Science Models, Laws, Mechanisms, and Theories Explain Natural Phenomena
• Science searches for cause and effect relationships to explain natural events. (2-PS1-4)
Crosscutting Concepts
Patterns
• Patterns in the natural and human designed world can be observed. (2-PS1-1)
Cause and Effect
• Events have causes that generate observable patterns. (2-PS1-4)
• Simple tests can be designed to gather evidence to support or refute student ideas about causes. (2-PS1-2)
Energy and Matter
• Objects may break into smaller pieces and be put together into larger pieces, or change shapes. (2-PS1-3)
Connections to Engineering,Technology, and Applications of Science
Influence of Engineering, Technology, and Science on Society and the Natural World
• Every human-made product is designed by applying some knowledge of the natural world and is built using materials derived from the natural world. (2-PS1-2)
Performance Expectations
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
2-PS1-1. Plan and conduct an investigation to describe and classify different kinds of materials by their observable properties. [Clarification Statement: Observations could include color, texture, hardness, and flexibility. Patterns could include the similar properties that different materials share.]
2-PS1-2. Analyze data obtained from testing different materials to determine which materials have the properties that are best suited for an intended purpose.* [Clarification Statement: Examples of properties could include, strength, flexibility, hardness, texture, and absorbency.] [Assessment Boundary: Assessment of quantitative measurements is limited to length.]
2-PS1-3. Make observations to construct an evidence-based account of how an object made of a small set of pieces can be disassembled and made into a new object. [Clarification Statement: Examples of pieces could include blocks, building bricks, or other assorted small objects.]
2-PS1-4. Construct an argument with evidence that some changes caused by heating or cooling can be reversed and some cannot. [Clarification Statement: Examples of reversible changes could include materials such as water and butter at different temperatures. Examples of irreversible changes could include cooking an egg, freezing a plant leaf, and heating paper.]*
Common Core State Standards Connections
ELA/Literacy
RI.2.1 Ask and answer such questions as who, what, where, when, why, and how to demonstrate understanding of key details in a text. (2-PS1-4)
RI.2.3 Describe the connection between a series of historical events, scientific ideas or concepts, or steps in technical procedures in a text. (2-PS1-4)
RI.2.8 Describe how reasons support specific points the author makes in a text. (2-PS1-2),(2-PS1-4)
W.2.1 Write opinion pieces in which they introduce the topic or book they are writing about, state an opinion, supply reasons that support the opinion, use linking words (e.g., because, and, also) to connect opinion and reasons, and provide a concluding statement or section. (2-PS1-4)
W.2.7 Participate in shared research and writing projects (e.g., read a number of books on a single topic to produce a report; record science observations). (2-PS1-1),(2-PS1-2),(2-PS1-3)
W.2.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. (2-PS1-1),(2-PS1-2),(2-PS1-3)
Mathematics
MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (2-PS1-2)
MP.4 Model with mathematics. (2-PS1-1),(2-PS1-2)
MP.5 Use appropriate tools strategically. (2-PS1-2)
2.MD.D.10 Draw a picture graph and a bar graph (with single-unit scale) to represent a data set with up to four categories. Solve simple put-together, take-apart, and compare problems using information presented in a bar graph. (2-PS1-1),(2-PS1-2)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Grade 2 - 2-PS1 Matter and Its Interactions" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 14, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Grade-2-2-PS1-Matter-and-Its-Interactions >