_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ESS2.A: Earth Materials and Systems
• Wind and water can change the shape of the land. (2-ESS2-1)
ESS2.B: Plate Tectonics and Large-Scale System Interactions
• Maps show where things are located. One can map the shapes and kinds of land and water in any area. (2-ESS2-2)
ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes
• Water is found in the ocean, rivers, lakes, and ponds. Water exists as solid ice and in liquid form. (2-ESS2-3)
ETS1.C: Optimizing the Design Solution
• Because there is always more than one possible solution to a problem, it is useful to compare and test designs. (secondary to 2-ESS2-1)
_________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Use the Template and Resource Links to Fulfill NGSS
l. Goals:
Essential Questions:
NGSS Note: Think, question, entertain ideas.
ll. Introductory Activities to Assess Prior Knowledge/And Later to Assess Comprehension
ESS2.A Earth Materials and Systems
A. Simple Activities - that assess students’ understanding of the effect of wind and water on land.
B. Brainstorming Session
Question: What are some places that have been affected by wind and water erosion you know about?
1. Break students down into groups of 3-4.
2. Ask students to generate a list of places that have been affected by wind and water and briefly decribe them (i.e. Grand Canyon).
3. Discuss
ESS2.B Plate Tectonics and Large-Scale System Interactions
A. Simple Activities - that assess students’ understanding of how Maps show where things are located.
Maps - Learning to Use Them Activity
Map Drawing Activity
Landforms and Waterways Poster Building
Illustrating Landforms Performance Task
llustrating Waterways Performance Task
ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes
A. Simple Activities - that assess students’ understanding of where water is on Earth.
Where is Water on Earth? Matching
Where There is Water on Earth - Coloring Page
lll. New Knowledge - Text
ESS2.A Earth Materials and Systems
A. Read about the effect of wind and water on land (i.e. erosion).
ESS2.B Plate Tectonics and Large-Scale System Interactions
A. Simple Activities - that assess students’ understanding of how Maps show where things are located.
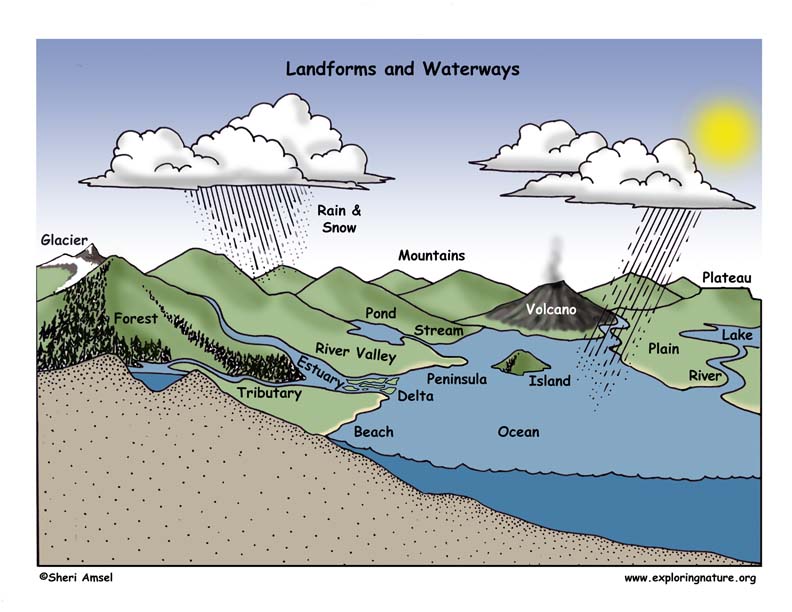
Landforms and Waterways
Landforms and Waterways Definitions Matching Quiz
Landforms and Waterways Vocabulary Matching Quiz
Waterways Coloring
ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes
A. Reading and Simple Activities - that advance student knowledge and assess students’ understanding of water on Earth.
The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes
Water on Earth - Mini-Poster
Phases of Matter – Gas, Liquids, Solids
Phases of Water - Matching
Phases of Water in Nature - Matching
Water Changing Phases Investigation - Diagram
Phases of Water in Nature - Mini-Poster
Examples of Models (depicts the concept expressed in the reading):
Ask students to look at the models of weather and nutrient cycle and explain how each illustrates the concept.
lV. Experiments, Activities, Model-making (Critical Thinking)
Inquiry related to Earth's waterways, landforms, and erosion:
Erosion Activity
Map Activity - Create a Landform Model
Water Changing Phases - Investigation
V. Summarize Knowledge - Enduring Understandings
Vl. Next Generation of Science Standards (NGSS) - Grade 2
Disciplinary Core Ideas
ESS2.A: Earth Materials and Systems
• Wind and water can change the shape of the land. (2-ESS2-1)
ESS2.B: Plate Tectonics and Large-Scale System Interactions
• Maps show where things are located. One can map the shapes and kinds of land and water in any area. (2-ESS2-2)
ESS2.C: The Roles of Water in Earth’s Surface Processes
• Water is found in the ocean, rivers, lakes, and ponds. Water exists as solid ice and in liquid form. (2-ESS2-3)ETS1.C: Optimizing the Design Solution
• Because there is always more than one possible solution to a problem, it is useful to compare and test designs. (secondary to 2-ESS2-1)
Science and Engineering Practices (NGSS)
Developing and Using Models
Modeling in K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to include using and developing models (i.e., diagram, drawing, physical replica, diorama, dramatization, or storyboard) that represent concrete events or design solutions.
• Develop a model to represent patterns in the natural world. (2-ESS2-2)
Constructing Explanations and Designing Solutions
Constructing explanations and designing solutions in K–2 builds on prior experiences and progresses to the use of evidence and ideas in constructing evidence-based accounts of natural phenomena and designing solutions.
• Compare multiple solutions to a problem. (2-ESS2-1)
Obtaining, Evaluating, and Communicating Information
Obtaining, evaluating, and communicating information in K–2 builds on prior experiences and uses observations and texts to communicate new information.
• Obtain information using various texts, text features (e.g., headings, tables of contents, glossaries, electronic menus, icons), and other media that will be useful in answering a scientific question. (2-ESS2-3)
Crosscutting Concepts
Patterns
• Patterns in the natural world can be observed. (2-ESS2-2),(2-ESS2-3)
Stability and Change
• Things may change slowly or rapidly. (2-ESS2-1)
Connections to Engineering,Technology, and Applications of Science
Influence of Engineering, Technology, and Science on Society and the Natural World
• Developing and using technology has impacts on the natural world. (2-ESS2-1)
Connections to Nature of Science
Science Addresses Questions About the Natural and Material World
• Scientists study the natural and material world. (2-ESS2-1)
Performance Expectations
Students who demonstrate understanding can:
2-ESS2-1. Compare multiple solutions designed to slow or prevent wind or water from changing the shape of the land.* [Clarification Statement: Examples of solutions could include different designs of dikes and windbreaks to hold back wind and water, and different designs for using shrubs, grass, and trees to hold back the land.]
2-ESS2-2. Develop a model to represent the shapes and kinds of land and bodies of water in an area. [Assessment Boundary: Assessment does not include quantitative scaling in models.]
2-ESS2-3. Obtain information to identify where water is found on Earth and that it can be solid or liquid.
Common Core State Standards Connections
ELA/Literacy
W.2.7 Participate in shared research and writing projects (e.g., read a number of books on a single topic to produce a report; record science observations).
(2-LS4-1)
W.2.8 Recall information from experiences or gather information from provided sources to answer a question. (2-LS4-1)
Mathematics
MP.2 Reason abstractly and quantitatively. (2-LS4-1)
MP.4 Model with mathematics. (2-LS4-1),(2-LS4-2)
2.MD.D.10 Draw a picture graph and a bar graph (with single-unit scale) to represent a data set with up to four categories. Solve simple put-together, take-apart, and compare problems using information presented in a bar graph. (2-LS4-2)
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Grade 2 - 2-ESS2 Earth’s Systems" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Grade-2-2-ESS2-Earthrsquos-Systems >