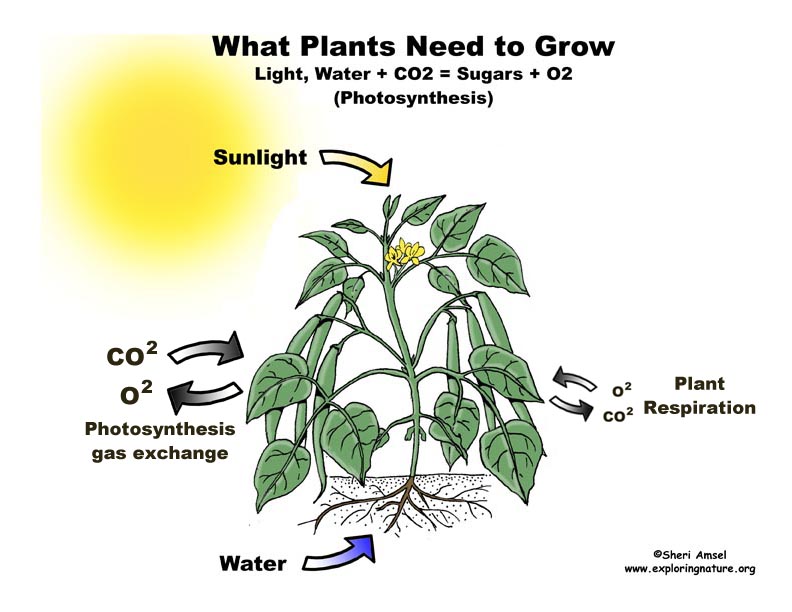
Plants depend on the sun for food. They use sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to make food to survive - to grow, flower and make seeds. Sunlight is collected on their leaves, which are the food-making part of a plant. Water is pulled up from the ground through their roots into their stems and leaves. Carbon dioxide is absorbed from the air through tiny holes under their leaves, called stomata. Plants use this sunlight, water and carbon dioxide to make sugars. The sugars are the food the plants use to grow – to make more plant matter. This is a chemical process called photosynthesis.
Animals need food in order to survive – to grow, heal, move, stay warm, and reproduce. They eat plants or other animals to get the energy they need. Animals break down their food into sugars for energy to move, proteins for growth and repair and fats to stay warm. It is important to note that because the sun drives the growth of plants, which provides the food for animals, animals depend on the sun for food too. Some animals eat only plants. They are called herbivores. Examples of herbivores are deer, beavers, elephants, and kangaroos. Some animals eat only other animals. These meat-eaters are called carnivores. Examples of carnivores are tigers, polar bears, lions and seals. Some animals eat both meat and plants. They are called omnivores. Examples of omnivores are raccoons, monkeys, possums and humans. There are even living things that eat dead animals and plants. They are called decomposers. Examples of decomposers are insects, bacteria, and fungi. Decomposers help break down and recycle dead matter into the soil. Those nutrients help plants grow. Everywhere on Earth, plants are making food, animals are eating it (and each other), and decomposers are recycling dead matter to enrich the soil where plants grow. These food webs drive all life on Earth.