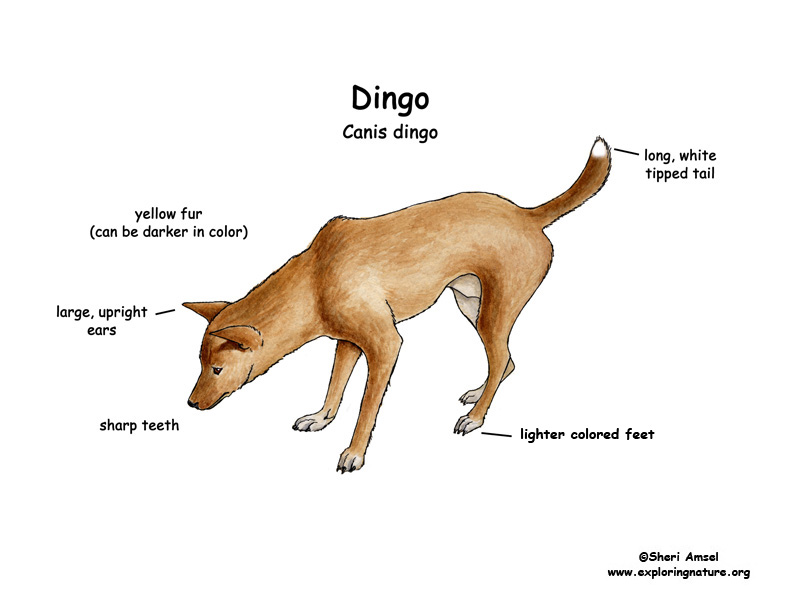
The dingo is the wild dog of Australia.
They live all over the desert and open dry country. They are usually a reddish-gold color.
Their ears stand up and they have a white tipped tail. Males can weigh up to 200 pounds, while females are smaller. Dingoes may have been brought to Australia by the aborigine thousands of years ago. It is believed that they descend from an Asian wild dog that cannot bark.
Dingoes live in packs. They hunt in the group and sometimes alone. Because of the heat in Australia most animals are active at night (nocturnal). So dingoes hunt at night when the animals are active. They are the largest, hunting mammal in Australia.
They eat many things from birds and mammals to carrion (dead animals).
Man.
Females are pregnant for about 9 weeks (gestation). They have up to 8 pups in August to October.
They live about 14 years. They are listed as "vulnerable".
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Carnivora
Suborder: Caniformia
Family: Canidae
Genus: Canis
Species: Canis lupus
Subspecies: Canis lupus dingo
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Dingo" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 14, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/Dingo >