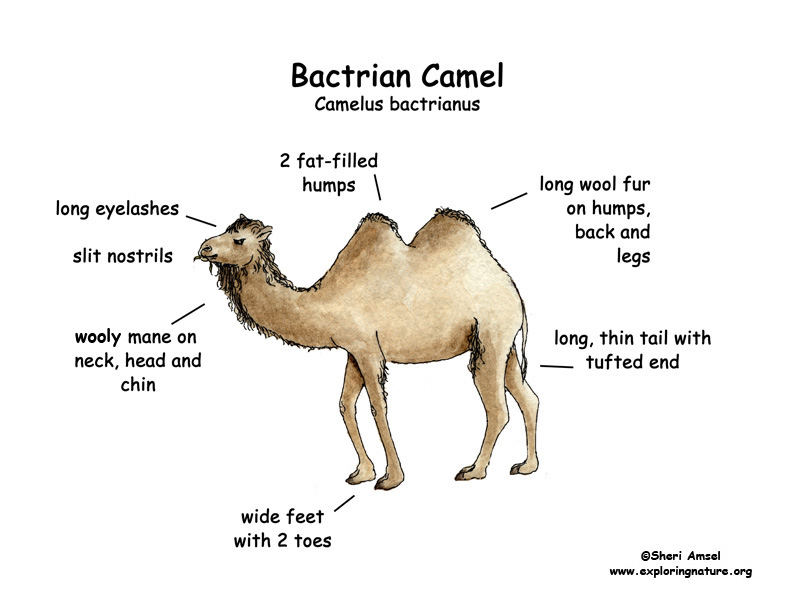
The camels that live in the deserts of Mongolia and China have 2 humps. They are also tamed (domesticated) and used as pack animals in Asia and Australia.
They are found on dry grasslands, in canyons and in mountainous areas. These are the camels of the Gobi desert.
Their bodies’ are10 feet long. They are 7 feet tall. The Bactrian camel’s two humps are filled with fat. Their humps sag after a long time without food and water. That is because their body breaks down the fat in their hump when it needs it. Like all camels, the Bactrian have wide feet for sand walking and eyelashes and tiny, thin nostrils for protection from blowing sand.
Camels can go for a long time without water. When they finally reach water they can drink a large amount at one time.
They eat grass, shrubs and leaves and other plants that are not good food for most mammals. They are herbivores.
No known predators.
They are pregnant for 12 - 15 months (gestation). They have 1 baby.
They can live for 40 years. They are considered endangered.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Artiodactyla
Family: Camelidae
Genus: Camelus
Species: Camelus bactrianus
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Camel (Bactrian)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 15, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/318 >