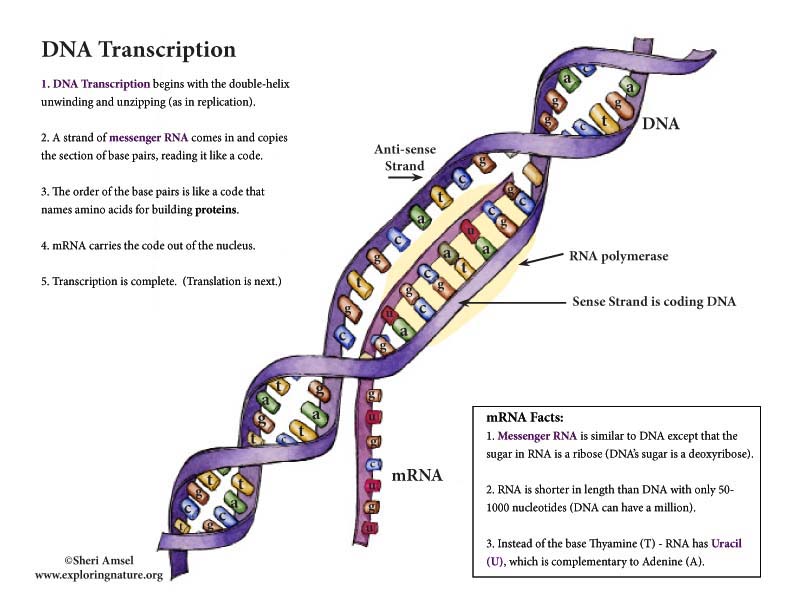
DNA Transcription also begins with the double helix unwinding and unzipping. Then a strand of material called messenger RNA (mRNA) comes in and copies the section of base pairs, reading it like a code.
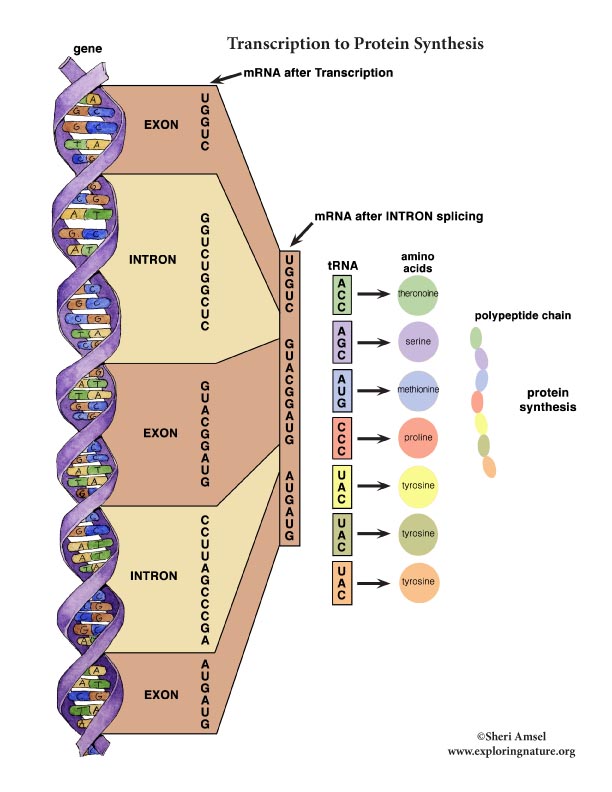
The order of the base pairs is like a code that names amino acids for building proteins. Three bases together are called a “codon.” Each codon spells out one amino acid. There are 64 possible codon combinations, but only 20 amino acids. The code has many overlaps. Many amino acids together build a specific protein. This is called protein synthesis and this is what is called your genetic code.
When the mRNA carries the code out of the nucleus it is much shorter than the DNA strand it copied. That is because:
Transcription is complete.
Collaborative consultation on website genetics and genomics from Dr. Stephen M. Carleton, Assistant Professor, Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, SUNY Health Science Center at Brooklyn.