They are found in Northern Africa. They were introduced to Australia in 1840 and have thrived in Australia's arid climate.
They live in the Sahara Desert in Northern Africa. They also live in Australia's arid outback.
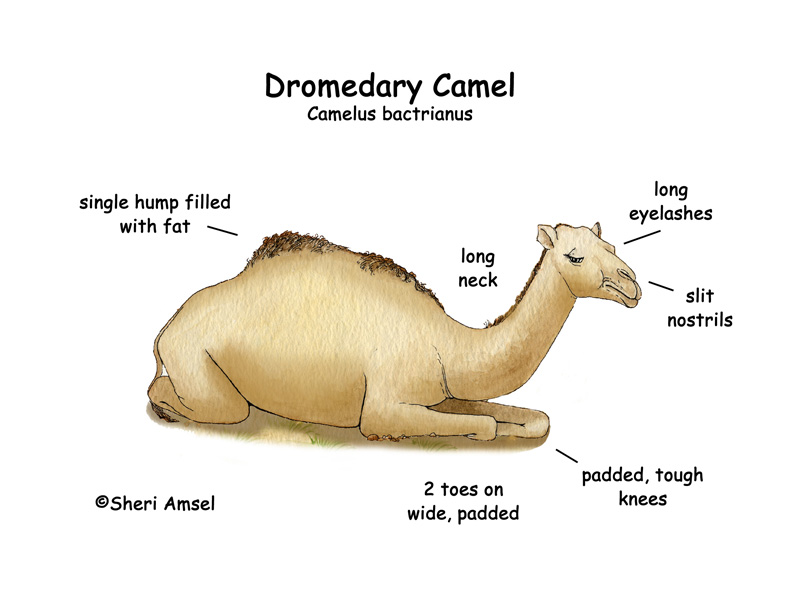
These one-humped, dromedary camels are mostly tame (domesticated) now. They are used for traveling in the desert. The camel’s hump is filled with fat. If they don’t have food for a long time the fat in their hump will begin to break down and be used by the body. Camels have a heavy fur coat that protects them from the heat. Their wide feet are made for walking on sand. They have thick eyelashes to protect their eyes from blowing sand. They also have thin, little nostrils to protect their nose from blowing sand. They weigh up to 1,500 pounds. They are 10 feet long.
Camels can go for a long time without water. When they finally reach water they can drink a large amount at one time. They have thrived in Australia's outback, where they now compete with native wildlife for water and food.
They eat any plant in the desert. They also will eat fish, meat and bones. They can drink salty water if that is all there is. They can drink 1/3 of their body weight very quickly when they finally reach water.
No known predators.
Females are pregnant for 13 months (gestation). They have 1 calf.
They can live for 30 - 40 years. They are not a threatened species and in fact are raised as domestic animals.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Artiodactyla
Family: Camelidae
Genus: Camelus
Species: Camelus dromedarius
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Camel (Dromedary)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 15, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/319 >