They are found along the continental shelves in all oceans throughout the world.
They live in coastal waters around islands, along the continental shelves and sometimes checking out bays and harbors. They have been known to travel down to more than 4,000 feet.
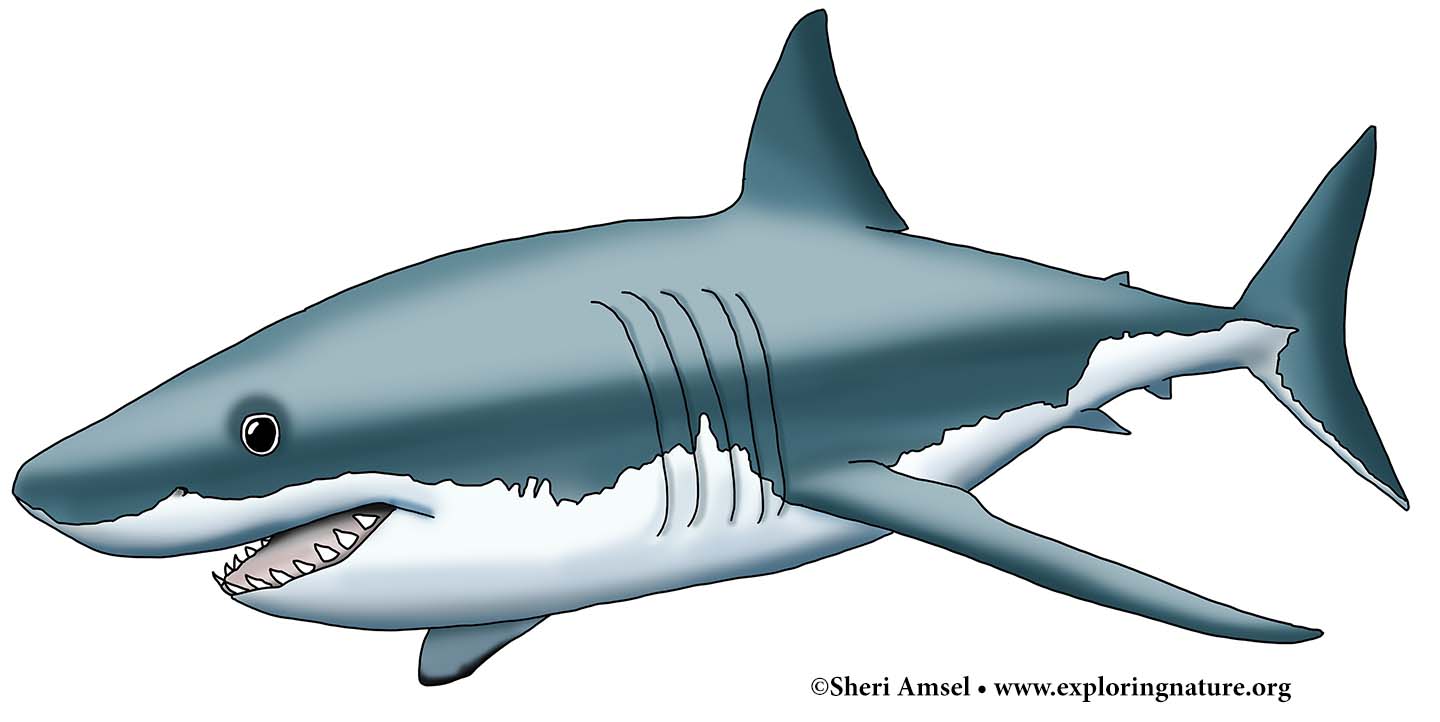
They can reach more than 20 feet long and weigh up to 2 tons (4,000 pounds). They are dark on top and white underneath. They have a large cone-shaped head with many rows of razor sharp teeth.
They travel alone. They are a fierce predator. They use their great sense of smell and eyesight to locate prey, but can also sense electrical currents in the water that are released by muscles when an animal is swimming.
They eat fish, sharks, seals and porpoises and even sea turtles.
The eggs hatch inside the female so young are born live (viviparous). They can have more than a dozen young 18 inches long.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Chondrichthyes
Order: Lamniformes
Suborder: None
Family: Lamnidae
Genus: Carcharodon
Species: C. carcharias
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Shark (Great White)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 14, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/609 >