They are found in the northern third of Australia and New Guinea.
They live in grassy areas and open forests near rivers and streams but also are found in mangroves along the coasts.
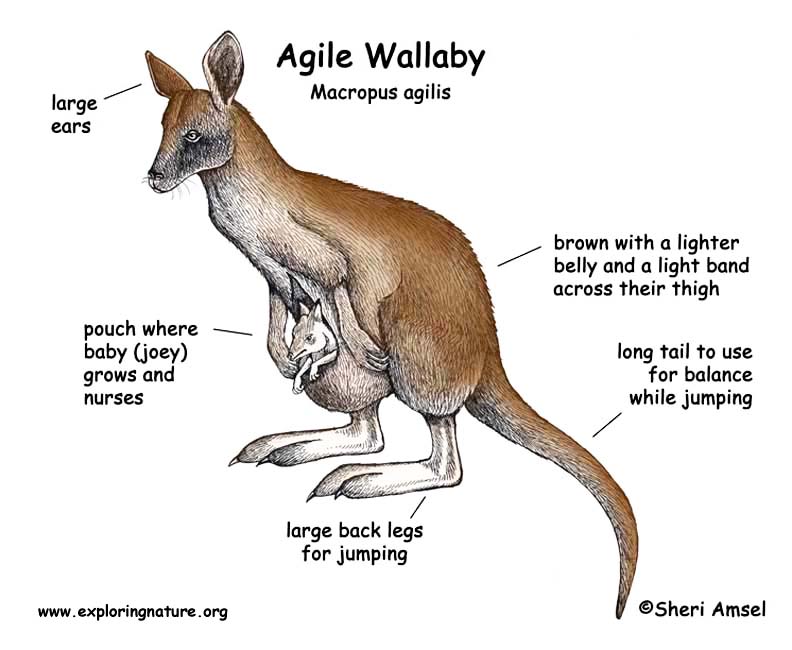
They are brown with a lighter belly. They have a white stripe across their thigh. Males are much larger than females standing more than 4 feet tall.
They are a solitary species of wallaby, though may gather in groups (mobs) to feed. They are good swimmers. They are easily startled and will panic if frightened and can injure themselves trying to escape predators. They sleep during the day and are active in the mornings, evenings and at night (nocturnal).
They eat grass, roots and insects.
They are hunted by dingos and man.
Females are only pregnant (gestation) for 1 month, but like kangaroos, the tiny babies develop in the pouch for many months.
They may live 12-15 years in the wild. They are listed as Lower Risk - least concern.
Kingdom: Animalia
Phylum: Chordata
Subphylum: Vertebrata
Class: Mammalia
Order: Diprotodontia
Suborder: Macropodiformes
Family: Macropodidae
Subfamily: Macropodinae
Genus: Macropus
Species: Macropus agilis
When you research information you must cite the reference. Citing for websites is different from citing from books, magazines and periodicals. The style of citing shown here is from the MLA Style Citations (Modern Language Association).
When citing a WEBSITE the general format is as follows.
Author Last Name, First Name(s). "Title: Subtitle of Part of Web Page, if appropriate." Title: Subtitle: Section of Page if appropriate. Sponsoring/Publishing Agency, If Given. Additional significant descriptive information. Date of Electronic Publication or other Date, such as Last Updated. Day Month Year of access < URL >.
Amsel, Sheri. "Wallaby (Agile)" Exploring Nature Educational Resource ©2005-2024. December 13, 2024
< http://www.exploringnature.org/db/view/389 >